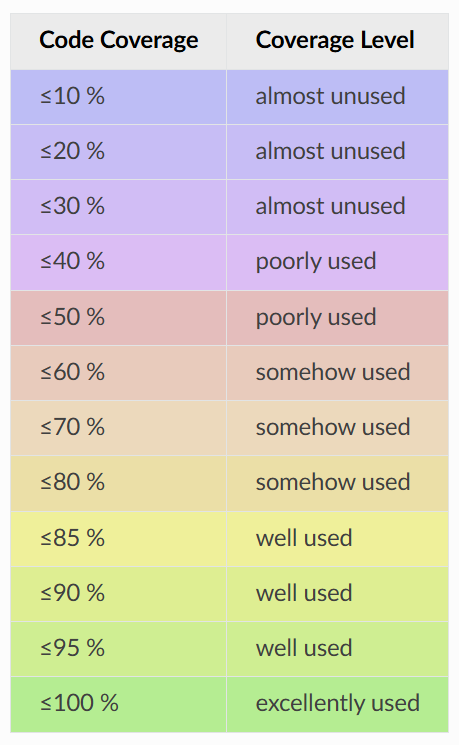
Code Coverage
The report:code-coverage directive generates a code coverage report summary table. The code coverage
report file(s) need to be configured in Sphinx’s conf.py for pre-analysis and data aggregation
(see below for details). This also allows the directive to supports multiple code coverage
reports per Sphinx documentation. Each code coverage report is referenced by the
reportid option, which matches the dictionary key used in the
configuration file.
Minimal Example
CodeCoverage.rst
.. report:code-coverage::
:reportid: src
Options
Additional options are offered for fine-tuning and styling of the report:
reportidReference the code coverage report file and settings as listed in
conf.py.no-branch-coverage(optional)If this flag is set, only statement coverage is shown.
class(optional)User-defined CSS class name(s), which are applied on the HTML table.
Supported Code Coverage Formats
Currently, only JSON output from Coverage.py (Python) can be read and visualized.
The pyEDAA.Reports projects works on a unified code coverage format, which can read, transform, merge and write any format (XML (Cobertura), JSON (Coverage.py), …). This would allow this directive to display any code coverage result.
Future Ideas
It’s planned to display a per package and per module code coverage on a separate Sphinx document (separate HTML page) with syntax highlighting and colored background visualizing the coverage status.
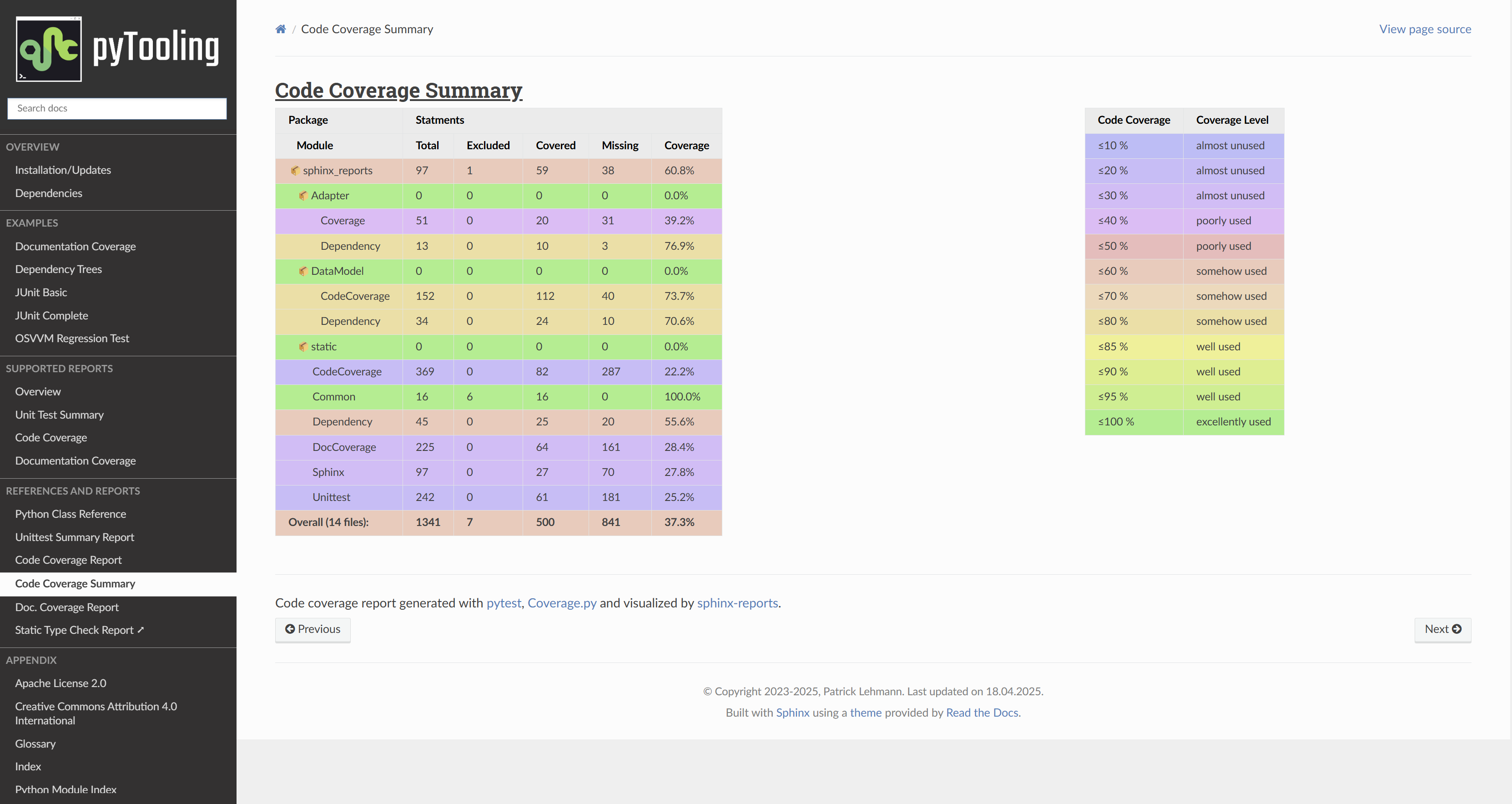
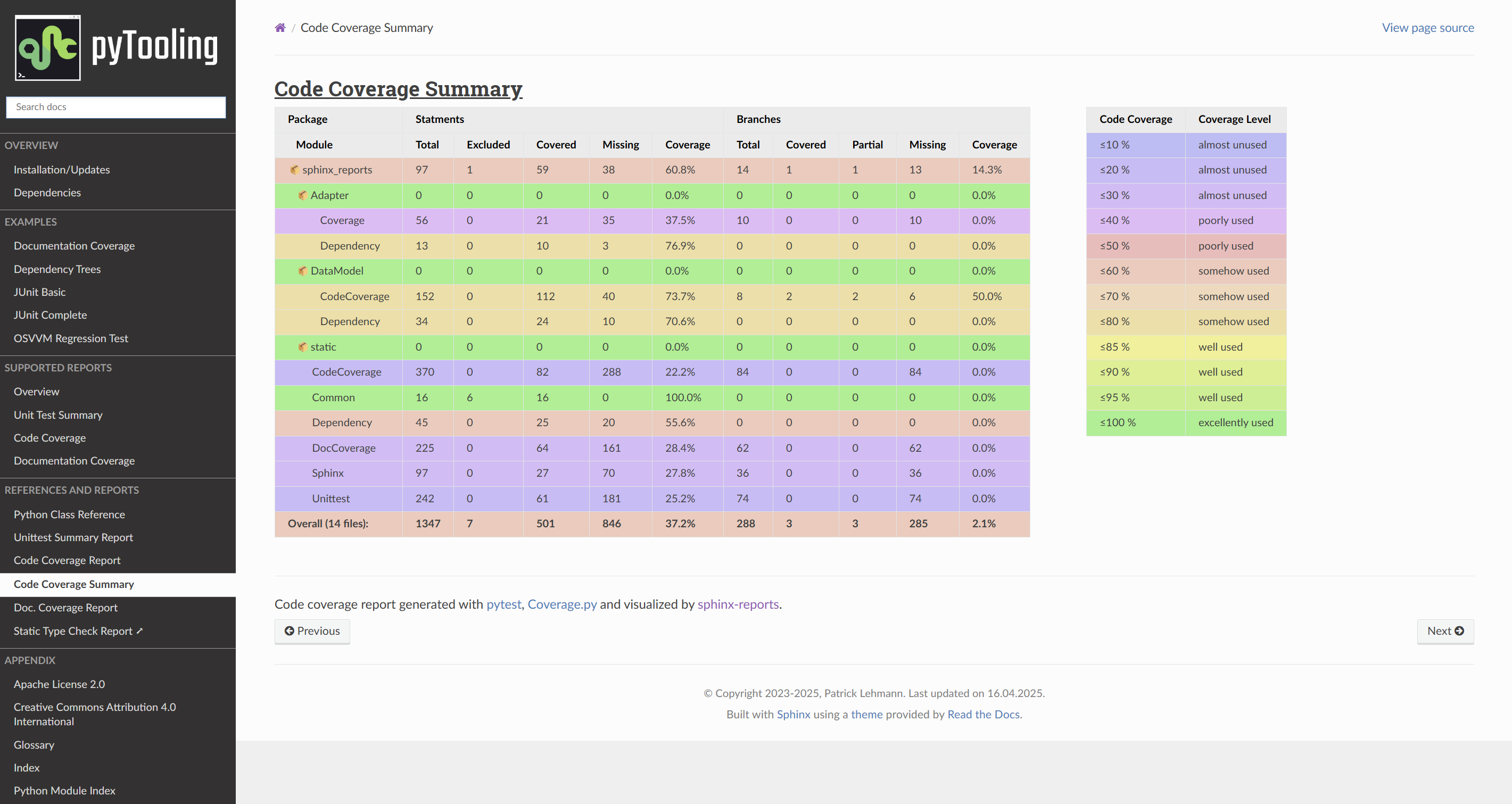
Configuration Entries in conf.py
See the overview page on how to setup and enable the sphinx-reports extension in general.
Configure one or more coverage analysis reports in conf.py by adding a new section defining some
configuration variables. Each analysis report is identified by an ID, which is later referred to by the report
directive or legend directive. Here, the ID is called src (dictionary key). Each analysis report needs 4
configuration entries:
nameName of the Python package [1].
json_reportThe code coverage report as JSON file as generated by Coverage.py.
fail_belowAn integer value in range 0..100, for when a code coverage is considered FAILED.
levelsEither a predefined color palett name (like
"default"), or
a dictionary of coverage limits, their description and CSS style classes.
# ==============================================================================
# Sphinx-reports - CodeCov
# ==============================================================================
report_codecov_packages = {
"src": {
"name": "myPackage",
"json_report": "../report/coverage/coverage.json",
"fail_below": 80,
"levels": "default"
}
}
# ==============================================================================
# Sphinx-reports - CodeCov
# ==============================================================================
report_codecov_packages = {
"src": {
"name": "myPackage",
"json_report": "../report/coverage/coverage.json",
"fail_below": 80,
"levels": {
30: {"class": "report-cov-below30", "desc": "almost unused"},
50: {"class": "report-cov-below50", "desc": "poorly used"},
80: {"class": "report-cov-below80", "desc": "medium used"},
90: {"class": "report-cov-below90", "desc": "well well"},
100: {"class": "report-cov-below100", "desc": "excellent used"},
"error": {"class": "report-cov-error", "desc": "internal error"},
}
}
}
Example Document
The following CodeCoverage.rst document is an example on how to use the report:code-coverage
directive. The first file consists of three parts:
A page title (headline)
A grid from sphinx{design} so
report:code-coverageandreport:code-coverage-legendcan be displayed side-by-sideA footer
The second file shows how to integrate that document into the navigation bar / toc-tree.
CodeCoverage.rst
.. _CODECOV:
Code Coverage Report
####################
.. grid:: 2
.. grid-item::
:columns: 8
.. report:code-coverage::
:reportid: src
.. grid-item::
:columns: 4
.. report:code-coverage-legend::
:reportid: src
:style: vertical-table
----------
Code coverage report generated with `pytest <https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest>`__, `Coverage.py <https://github.com/nedbat/coveragepy/tree/master>`__ and visualized by `sphinx-reports <https://github.com/pyTooling/sphinx-reports>`__.
index.rst
.. toctree::
:caption: References and Reports
:hidden:
Python Class Reference <sphinx_reports/sphinx_reports>
Unittest
CodeCoverage
Doc. Coverage Report <DocCoverage>
Static Type Check Report ➚ <typing/index>
.. toctree::
:caption: Appendix
:hidden:
Sphinx Directives
The following directives are provided for visualizing code coverage reports.
- .. report:code-coverage::
Generate a table summarizing the code coverage per Python source code file (packages and/or modules). The package hierarchy is visualized by indentation and a 📦 symbol.
- :class:
Optional: A list of space separated user-defined CSS class names.
The CSS classes are applied on the HTML
<table>tag.
- :reportid:
An identifier referencing a dictionary entry (key) in the configuration variable
report_codecov_packagesdefined inconf.py.
- :no-branch-coverage:
If flag is present, no branch coverage columns are shown. Only statement coverage columns are present.
- .. report:code-coverage-legend::
Generate a table showing the color palett applied to a code coverage summary table.
Each code coverage report could potentially use its own color palett. Therefore, the
reportidoptions should use the same values.- :class:
Optional: A list of space separated user-defined CSS class names.
The CSS classes are applied on the HTML
<table>tag.
- :style:
Specifies the legend style. Default is
horizontal-table.Possible values:
defaulthorizontal-tablevertical-table
Sphinx Roles
There are no roles defined.
Color Paletts
The default color palett can be changed by:
setting a different predefined color palett name.
specifying a new list of coverage level which also define a corresponding CSS class name.
overriding the existing CSS rules with different colors and styles.
default palett
The default palett defines 12 levels: ≤10%, ≤20%, ≤30%, ≤40%, ≤50%, ≤60%, ≤70%, ≤80%, ≤85%, ≤90%, ≤95%, ≤100%
from blue via red, orange, yellow to green.
Custom CSS Styling
Table Styling
The table-tag has 2 additional CSS classes:
report-codecov-tableAllows selecting the
tabletag, but only for code coverage reports.report-codecov-%reportid%Allows selecting one specific code coverage report.
%reportid%gets replaced by the reportid used in the option field of the directive. Here it got replaced bysrc.
Row Styling
The tr-tag (table row) has 2 additional CSS classes:
report-package/report-module/report-summaryThis class indicated if the row refers to a Python package, Python module or the overall coverage summary (last row).
report-below-%percentage%Depending on the coverage in percent, a CSS class is added according to the color palett configuration.
<table class="report-codecov-table report-codecov-src">
<thead>
<tr>
<th> ..... </th>
.....
<th> ..... </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr class="report-package report-below-30"> ..... </tr>
<tr class="report-module report-below-70"> ..... </tr>
.....
<tr class="report-summary report-below-50"> ..... </tr>
</tbody>
</table>
table.report-codecov-table > thead > tr,
table.report-codecov-legend > thead > tr {
background: #ebebeb;
}
table.report-codecov-table > tbody > tr.report-cov-below95,
table.report-codecov-legend > tbody > tr.report-cov-below95 {
background: hsl(90 75% 75%);
}
table.report-codecov-table > tbody > tr.report-summary {
font-weight: bold;
}
Footnotes